Redis in .Net
Introduction
We are going to discuss Caching in .NET and how it works. So, we look at the following things one by one.
Introduction of Caching
What is Cache
Types of cache
Cache Implementation
Caching is very popular nowadays in the software industry because it will improve the performance and scalability of the application. We use many web applications like Gmail and Facebook, and we see how responsive they are. We have a great user experience. There are a lot of users using the internet and if an application has huge network traffic and demand, we need to take care of many things which help us to improve the performance and responsiveness of the application. So, because of that, there is the solution of caching, and that’s why caching comes into the picture.
So, let’s start one by one.
What is Caching?
The cache is the memory storage that is used to store the frequent access data in the temporary storage, it will improve the performance drastically avoid unnecessary database hits and store frequently used data into the buffer whenever we need it.
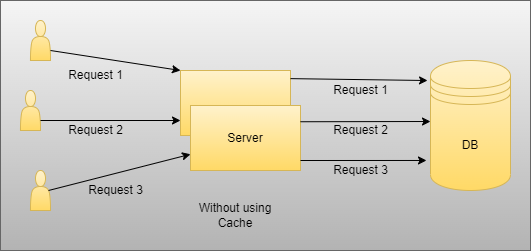

As you see in the above image, there are two scenarios, one is without using cache, and another is with cache. So here, when we do not use the cache, in that case, suppose users want data, then they will hit each time database, and it will increase the time complexity and reduce performance in case there is some static data users want, and it is the same for all users. In that case, when we do not use cache, then each one hits the unnecessary database to fetch data. On the other side, as you can see, we use the cache, and in that case, if there is the same static and the same data for all users, then only the first user will hit the database, fetch data, and store it into the cache memory and then other two users used that from the cache without unnecessarily hit database to fetch data.
Types of Cache
Basically, there are two types of caching .NET supports.
In-Memory Caching
Distributed Caching
When we use In-Memory Cache then in that case data is stored in the application server memory, and whenever we need then, we fetch data from that and use it wherever we need it. And in Distributed Caching, there are many third-party mechanisms like Redis and many others. But in this section, we look into the Redis Cache in detail and how it works in the .NET
Distributed Caching
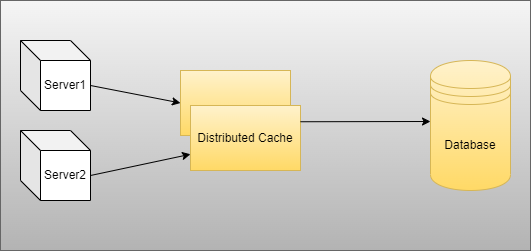
Basically, in distributed caching,g data are stored and shared between multiple servers
Also, it’s easy to improve the scalability and performance of the application after managing the load between multiple servers when we use a multi-tenant application
Suppose, In the future, if one server crashes and restarts then the application does not have any impact because multiple servers are as per our need if we want
Redis is the most popular cache, which is used by many companies nowadays to improve the performance and scalability of the application. So, we are going to discuss Redis and its usage one by one.
Redis Cache
Redis is an Open Source in-memory Data Structure store used as a database.
Basically, it is used to store the frequently used and some static data inside the cache and use and reserve that as per user requirement.
There are many data structures present in the Redis which we are able to use like List, Set, Hashing, Stream, and many more to store the data.
Installation of Redis Cache
Step 1. Download the Redis Server using the following URL.
https://github.com/microsoftarchive/redis/releases/tag/win-3.0.504
Step 2. Extract the zip file and later on open the Redis Server and Redis CLI.

Implementation of Redis Cache using .NET
Step 1. Create the .NET Web Application
Step 2. Install the following NuGet Packages, which need step by steps in our application
- StackExchange.Redis
Step 3. Add Line in ServiceExtension class in your project
services.AddStackExchangeRedisCache(options => { options.ConfigurationOptions = new StackExchange.Redis.ConfigurationOptions { EndPoints = { { "localhost", 6379 } }, Password = "jagadish" }; });
Step 4. Now, we are going to create the IRedisService Interface and RedisService Class for Redis Cache-related usage.
namespace DecentralizedVotingSystem.Core.Contracts.IServices;
public interface IRedisService <T> where T : class
{
Task<bool> CreateCache(List<T> model);
Task<List<T>> GetCache();
Task<bool> DeleteCacheById(int Id);
}
namespace DecentralizedVotingSystem.Infrastructure.Services;
public class RedisService<T>(IDistributedCache distributedCache) : IRedisService<T> where T : class
{
private readonly IDistributedCache _distributedCache = distributedCache;
private const string cacheKey = "DecentralizedVotingSystem";
public async Task<bool> CreateCache(List<T> model)
{
string? cachedData = await _distributedCache.GetStringAsync(cacheKey);
List<T> data = [];
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(cachedData))
{
data = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<List<T>>(cachedData) ?? [];
}
data.AddRange(model);
var validateData = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(data);
var cacheEntryOptions = new DistributedCacheEntryOptions
{
AbsoluteExpirationRelativeToNow = TimeSpan.FromDays(1)
};
await _distributedCache.SetStringAsync(cacheKey, validateData, cacheEntryOptions);
return true;
}
public async Task<List<T>> GetCache()
{
var cachedData = await _distributedCache.GetStringAsync(cacheKey);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(cachedData))
{
return null!;
}
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<List<T>>(cachedData) ?? [];
}
public async Task<bool> DeleteCacheById(int Id)
{
var cachedData = await _distributedCache.GetStringAsync(cacheKey);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(cachedData))
{
return false;
}
var data = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<List<T>>(cachedData) ?? [];
var itemToRemove = data.Find(item => (item as dynamic).Id == Id);
if (itemToRemove != null)
{
data.Remove(itemToRemove);
var updatedData = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(data);
await _distributedCache.SetStringAsync(cacheKey, updatedData);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
Step 5. Create the RedisControllerclass and create the following method as shown below.
namespace DecentralizedVotingSystem.API.Controllers;
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class RedisController(IRedisService<ValidateUpdateUserVm> redisService) : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IRedisService<ValidateUpdateUserVm> _redisService = redisService;
[HttpPost("createcache")]
public async Task<ActionResult> CreateCache(List<ValidateUpdateUserVm> validateUpdateUser)
{
try
{
bool cachedData = await _redisService.CreateCache(validateUpdateUser);
return cachedData ? Ok("Cache created successfully") : BadRequest("Data already cached");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Log.Error(ex.Message, ex);
return BadRequest("Unable Create Cache");
}
}
[HttpGet("getcache")]
public async Task<ActionResult> GetCache()
{
try
{
var cachedData = await _redisService.GetCache();
return cachedData == null ? Ok("No cached data found") : Ok(cachedData);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Log.Error(ex.Message, ex);
return BadRequest("Unable Retrieve Cache");
}
}
}
RedisInsight
RedisInsight is a visual tool provided by Redis that helps developers and administrators interact with Redis databases. It provides an intuitive GUI to inspect and manage Redis data, optimize queries, and monitor performance.
Benefits of RedisInsight:
Data Visualization: RedisInsight lets you view the data stored in Redis in a structured format, such as keys, lists, or hashes.
Performance Monitoring: Provides insights into how Redis is performing and offers tips to optimize operations.
Query Testing: Helps developers run and test queries directly, making it easier to debug and verify data operations.
Editing Data: You can edit, update, or delete cached data directly within RedisInsight without needing to write custom scripts.
Conclusion
Caching is a crucial mechanism in modern application development to enhance performance and scalability. By temporarily storing frequently accessed or static data, caching reduces unnecessary database hits, significantly improving response times and user experience. In .NET applications, developers can choose between In-Memory Caching and Distributed Caching based on the specific requirements of their application.
Among distributed caching solutions, Redis stands out as a highly efficient, open-source, in-memory data structure store. Redis not only offers high performance but also supports multiple data structures like lists, sets, and hashes, making it flexible for diverse caching needs. By implementing Redis in .NET, as demonstrated in this example, developers can create, retrieve, and manage cached data seamlessly using the StackExchange.Redis library.
Happy Coding!